PEDIATRIC SURGICAL CONDITIONS TREATED
- APPENDICITIS
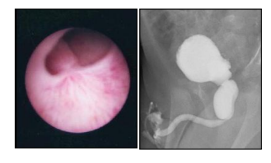
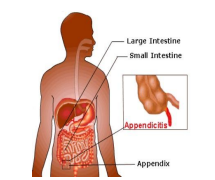
The inflammation of the appendix is called as appendicitis. Appendix is a small tubular structure present at the junction of the small and large intestine. The exact function of the appendix is not known. Blockage of the appendix leads to pain and vomiting. Mild appendicitis may resolve with antibiotics but there are chances of recurrence of the symptoms. Most of the time surgery is needed. It can be done with open appendectomy or with laparoscopy.
- CONGENITAL DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIA
presence of abdominal content in the thorax is called since birth is called congenital diaphragmatic hernia. It is due to defect in the diaphragm which separates the thorax and the abdomen. Correction of the defect is necessary to prevent respiratory problems and intestinal obstruction. The surgery can be done through chest or abdomen.
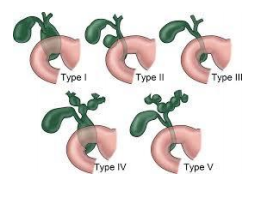
- CHOLEDOCHAL CYST
Choledochal cyst is one of the common abnormalities that affect the biliary system of children who present with complaints of upper abdominal pain and jaundice. Choledochal cyst may lead to recurrent cholangitis, biliary obstruction, stone and cancer. Excision of the entire cyst and restoring the bile flow.
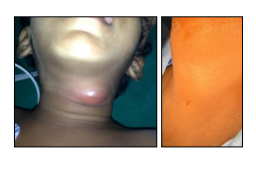
- BRANCHIAL CYST & SINUS
These may appear as swelling or sticky discharge in the neck. They may painless or painful. Discharge may increase during common cold. These needs excision as they may cause recurrent infection and painful swelling. They may develop in to cancer in later age.
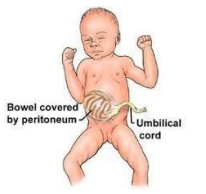
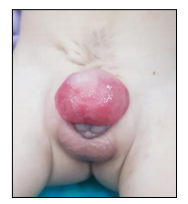
- OMPHALOCELE
An omphalocele is a covered defect of the umbilicus (belly button) with a “sac” which contains abdominal contents. The skin and the muscle of the abdomen are missing. This problem is thought to start in the third week of development when the intestines elongate and normally reside in the yolk sac outside of the abdomen. Omphaloceles are covered by a sac composed of an outer layer and an inner layer. The umbilical cord s right into the sac. A separate compartment containing a jelly-like material also may be observed. If the omphalocele is above the umbilicus there may be other defects involving the diaphragm, sternum, and heart. If the omphalocele is below the umbilicus there may be other defects affecting the bladder, rectum, and lower spinal cord. Omphalocele is associated with various congenital defects.
- FOREIGN BODY IN THE GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT
Ingestion of foreign bodies is a problem because of the tendency for small children to put everything into their mouths. There may or may not be history of ingestion of a foreign body. Most of the objected that are not very sharp and pass into the stomach do not cause problem and are excreted out in stools. Objects that are sharp and pointed have tendency to cause perforation. In cases where there is pain, obstruction or vomiting may need surgical intervention.
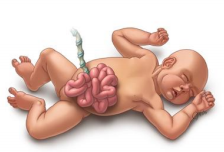
- GASTROSCHISIS
Gastroschisis is a condition in which the abdominal wall of the newborn fails to close at the umbilicus and hence the intestine of the baby lies outside the abdomen and exposed. The intestine should be returned inside the abdominal cavity.
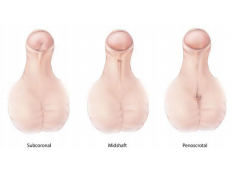
- HYPOSPADIAS
When the pee hole of baby boy is away from the normal position on the tip, it is called hypospadias. Hypospadias surgery involves correction of any abnormal curvature of the penis, creation of normal looking tip of penis and creating the pee hole at the normal position. This can be done in single stage or multiple stages depending on the original position and curvature of the penis.
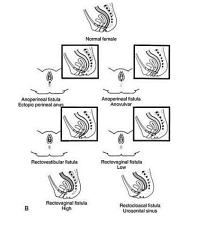
- FEMALE ANORECTAL MALFORMATIONS
Absence of the anal opening in the normal position is called ano-rectal malformation. There are different types of anomalies depending on sex of the child, position of the anal opening, absence of anal opening etc. hence there are different methods of correction of the defects.
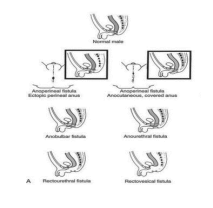
- MALE ANORECTAL MALFORMATIONS
Absence of the anal opening in the normal position is called ano-rectal malformation. There are different types of anomalies depending on sex of the child, position of the anal opening, absence of anal opening etc. hence there are different methods of correction of the defects.
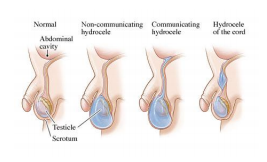
- HYDROCELE
The occurrence of a congenital inguinal hernia and undescended testis is related to descent of the testis into the scrotum. The testes start developing in the abdomen and eventually drop into the scrotum. As the testes drop into the scrotum a membrane surrounding all the abdominal contents gets pulled into the scrotum with the testes. This is called the processus vaginalis. At approximately 3 months’ gestation, the testis descends into the scrotum because of the influence of hormones. The testes usually reach its final destination in the scrotum by the third trimester. In approximately 90% of children, the processus vaginalis seals shut and become a thin band of tissue without a lumen or opening. If all or any portion of the processus remains open it may cause a congenital inguinal hernia, hydrocele or a communicating hydrocele. (Fig. 42-1). The frequency that the processus vaginalis remains open is related to the gestational age of the infant and whether the testis drops into the scrotum or not. In girls, hernias are less common than in boys though inguinal hernia and, more rarely, a hydrocele may occur.
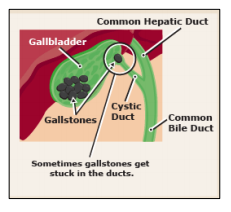
- GALL STONES
Recently there is increase in the incidence of gall stones in children. Usually they are without any complaints but sometimes may lead to blockage of the bile flow and cause pain, jaundice and fever. Gallstones may be associated with sickle cell anemia.
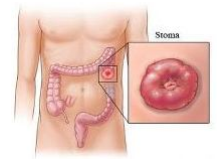
- COLOSTOMY
The need to have one’s gallbladder removed is generally due to the formation of gallstones. Gallstones form when there is an imbalance in the components in the bile that is normally stored in the gallbladder. For most people, there is no known reason why gallstones develop. Nevertheless, there are diseases that can predispose your child to form gallstones. Children who have problems with blood cells being broken down easily such as can happen in spherocytosis and sickle cell anemia have increased incidence of gallstone formation.
- EPISPADIAS
Inflammation and/or infection of the Epididymis and testis are called Epididymitis and Orchitis. In adults is mostly due to sexually transmitted diseases. But in children it associated with urinary tract anomalies. Any infection of the testis needs prompt administration of antibiotics and analgesics. Further investigations are warranted to find out any urinary tract anomaly.
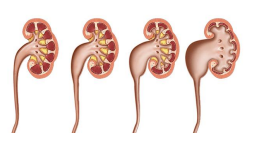
- HYDRONEPHROSIS
Acute swelling of the gallbladder in the absence of gallstones is a well-recognized problem. Hydrops may occur as a newborn and in older children. This condition is characterized by the development of a fluid collection around the gallbladder and main bile duct that drains the liver. Hyperinsulinism
Congenital hyperinsulinism, also called nesidioblastosis, is a problem in babies in which insulin control is abnormal, causing low blood sugar. Patients with this syndrome may have signs of low blood sugar without actually having a high insulin level, showing that they have a problem with insulin control.